A header tag is an HTML element that defines the headings on a webpage. These tags, ranging from H1 to H6, play a crucial role in structuring content, making it more readable for both users and search engines.
Header tags are hierarchical, with the H1 tag representing the main heading of the page. This primary heading holds the utmost importance, summarizing the core topic or theme of the content. Search engines use the H1 tag to understand the primary focus of the page, influencing how the content is indexed and ranked.
As we move down the hierarchy, H2 tags come into play as subheadings. These tags divide the content into sections, offering a clear structure that aids both users and search engines in navigating through the material. H3, H4, H5, and H6 tags further refine this organizational structure.
Proper usage of header tags not only improves the organization of content but also contributes significantly to search engine optimization. Search engines rely on these tags to understand the context and relevance of the content, helping them index and rank web pages accurately.
One key aspect of header tag optimization is the strategic inclusion of relevant keywords. Incorporating keywords naturally within your header tags signals to search engines what the content is about, aiding in better ranking for relevant queries.
Types of Header Tags
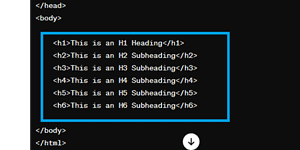
H1 - The Main Heading
The H1 tag represents the primary heading of a webpage. It typically introduces the main topic or theme of the content. Search engines give significant weight to the H1 tag, considering it the most important heading on a page.
H2 - Subheadings
H2 tags serve as subheadings, providing a clear structure beneath the H1. These subheadings help break down the content into distinct sections, making it easier for readers to navigate and comprehend.
H3 - Further Sub-divisions
H3 tags offer a more granular breakdown of the content. They can be used to create additional subheadings beneath H2 headings, contributing to a more detailed and organized structure.
H4 - Additional Subheadings
H4 tags provide an even more refined level of subdivision. While not as commonly used as H1 to H3, H4 headings can be effective for categorizing content within the broader sections.
H5 and H6 tags - Leeser Used
H5 and H6 tags are less commonly used but can be employed for further subdivision within the content hierarchy. They offer flexibility for creating a detailed and intricate structure when necessary.
Importance of Header Tag in SEO?
Header tags are indispensable elements in the world of Search Engine Optimization (SEO), playing a crucial role in enhancing a website's visibility and overall ranking on search engine result pages (SERPs). These HTML tags, ranging from H1 to H6, contribute significantly to the structural organization of content, making it more comprehensible for both users and search engine algorithms.
First and foremost, the H1 tag serves as the main heading of a page, providing a concise and direct summary of the content's primary theme. Search engines give considerable importance to the H1 tag, using it as a key indicator to understand the main focus of the page. This strategic use of the H1 tag assists search engines in indexing and ranking the content accurately.
Beyond the H1 tag, subheadings (H2 to H6) play a crucial role in further breaking down the content into logical sections. This hierarchical structure not only improves the overall readability for users but also aids search engines in comprehending the relationships between different parts of the content. Consistency in header tag usage helps establish a clear information hierarchy, which is a key factor in SEO.
Properly optimized header tags also contribute to keyword relevance, another vital aspect of SEO. Including relevant keywords in header tags signals to search engines the core topics covered in the content, aligning with the user's search intent. This can lead to improved rankings for specific queries, driving more organic traffic to the website.
Difference between head and header tag
The "head" and "header" tags are distinct HTML elements serving different purposes in web development. Let's delve into the key differences between them:
Purpose:
Head Tag:
The <head> tag is primarily used to contain metadata about the HTML document, such as the title, character set, links to stylesheets, scripts, and other essential information that doesn't directly appear on the webpage.
Header Tag:
On the other hand, the <header> tag is used to define introductory content within a document or a section. It typically includes headings, logos, navigation menus, or any content that introduces the main body of the webpage.
Content Location:
Head Tag:
The <head> tag is placed within the <html> element but before the <body> element. It is not visible on the webpage and is dedicated to providing information for browsers and search engines.
Header Tag:
The <header> tag is placed within the <body> element and contains content that is visible on the webpage. It is usually located at the top of a page or within a specific section, serving as an introduction to the main content.
Typical Usage:
Head Tag:
Common elements within the <head> tag include <title>, <meta> for character set and viewport settings, <link> for stylesheets, and <script> for JavaScript files.
Header Tag:
The <header> tag typically contains elements like <h1> for the main heading, logos, navigation menus, and other introductory content.
SEO Impact:
Head Tag:
Elements within the <head> tag, such as the <title> and meta tags, significantly impact SEO by providing information to search engines about the content and purpose of the webpage.
Header Tag:
While the <header> tag itself doesn't directly impact SEO, the content within it, especially the main heading and navigation links, contributes to the overall user experience and can indirectly influence search engine rankings.
The <head> tag focuses on metadata and document settings that are not directly visible on the webpage, while the <header> tag is used to define introductory content that is visible to users at the beginning of a document or within a specific section.
How to Add Header Tags in HTML
Adding header tags in HTML is a straightforward process that involves using specific elements to structure and organize the content of a webpage. Here's a step-by-step guide on how to add header tags:
Open Your HTML File:
Begin by opening the HTML file in which you want to add header tags using a text editor or an integrated development environment (IDE).
Choose the Appropriate Header Tag:
Determine the level of importance of the heading you want to add. HTML provides six levels of header tags, from H1 to H6, with H1 being the most important and H6 being the least.
Start the Header Tag:
To add an H1 tag, use the following syntax:
How to use header tags in SEO?
Replace "This is an H1 Heading" with your desired heading text. Similarly, you can use H2 to H6 tags by replacing "h1" with the appropriate tag name.
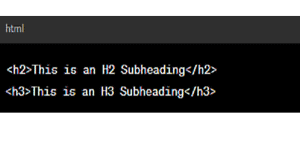
Add Subheadings:
To add subheadings beneath the main heading, use H2 to H6 tags accordingly. For example:
Save Your HTML File:
Once you've added the desired header tags, save your HTML file.
Preview Your Webpage: Open your HTML file in a web browser to preview how the header tags appear on the webpage. You should see the headings displayed in accordance with their respective levels of importance.
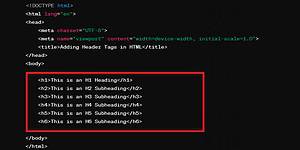
Here's a complete example of how header tags can be added to an HTML file:
Best Practices for Optimizing Header Tags
Add keyowrds in your Header Tag
Incorporate relevant keywords naturally into your header tags. This helps search engines understand the topic of your content and improves the chances of ranking for relevant searches.
Focus on H1 Tag:
Place your primary keyword or key phrase in the H1 tag, which represents the main heading of your page. This signals to search engines the primary topic or theme of your content, enhancing its relevance for related searches.
Keyword Variations:
Use variations of your target keywords across different header tags, especially in H2 and H3 subheadings. This allows you to cover a broader range of relevant search queries while maintaining a consistent thematic focus.
Long-tail Keywords:
Incorporate long-tail keywords or phrases into your header tags, especially in H2 to H6 headings. Long-tail keywords are more specific and can attract targeted traffic with higher conversion potential.
Avoid Keyword Stuffing:
While it's essential to include keywords in your header tags, avoid overusing them or stuffing them unnaturally into your content. Focus on creating headings that are descriptive, informative, and engaging for users while incorporating keywords in a meaningful way.
Avoid stuffing header tags with excessive keywords or irrelevant content. Header tags should be used judiciously to highlight the most important sections of your content, rather than as a means of keyword manipulation.
Featured Snippets
Header tags play a crucial role in supporting featured snippets, which are concise summaries of information displayed at the top of search engine results pages (SERPs). By structuring content with clear and descriptive header tags, websites increase their chances of being selected for featured snippets.
Search engines often use header tag content to generate these snippets, particularly when the headings directly answer common user queries. Including relevant keywords and providing succinct, informative content within header tags enhances the likelihood of a webpage being featured, ultimately driving more organic traffic and improving visibility in search results.
Header tags, such as H1, H2, and H3, play a pivotal role in the generation of featured snippets, which are concise summaries displayed prominently atop search engine results. These tags provide a clear structure to webpage content, aiding search engine algorithms in understanding the hierarchy and relevance of information.
When header tags contain concise and informative text that directly addresses common user queries, search engines are more likely to extract this content for featured snippets.
Therefore, strategically crafting header tag content to align with frequently searched topics increases the chances of a webpage being featured, ultimately boosting visibility and attracting more organic traffic from search results.
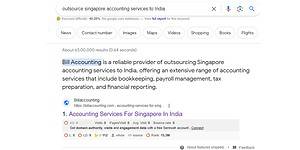
Here is example for Paragraph featured snippet
Don't Use more than one H1 tag
Using more than one H1 tag in a webpage can confuse search engines and hinder SEO efforts.
It's crucial to maintain a single H1 tag for the main heading, emphasizing the primary topic or theme of the content.
Utilize H2, H3, and other header tags to organize subheadings and further delineate sections, ensuring a clear and structured hierarchy that enhances both user experience and search engine optimization.
Keep Relevant Content in Headers:
Ensure that the content under each header tag is relevant to the heading.
Header tags should accurately reflect the topic or theme of the content that follows them, providing clear guidance to both users and search engines.
When users navigate a webpage, they rely on header tags to quickly grasp the main topics and structure of the content. Therefore, it's essential that the content following each header tag aligns with the heading's topic or theme.
For instance, if an H2 tag is used to introduce a subsection on "Benefits of Exercise," the content immediately following should discuss various advantages of physical activity, such as improved cardiovascular health, enhanced mood, and increased energy levels. This ensures consistency and clarity, helping users quickly find the information they're seeking.
Relevant content in headers contributes to better SEO performance. Search engines analyze the relationship between header tags and the content that follows to determine the relevance and quality of a webpage.